Complex Integration
The magic and power of calculus ultimately rests on the amazing fact that differentiation and integration are mutually inverse operations. And, just as complex functions enjoy remarkable differentiability properties not shared by their real counterparts, so the sublime beauty of complex integration goes far beyond its real progenitor.
Contour integral
Consider a contour $C$ parametrized by $z(t) = x(t) + i y(t)$ for $a\leq t\leq b.$ We define the integral of the complex function along $C$ to be the complex number \begin{eqnarray}\label{contour-integral} \int_C f(z)\,dz = \int_a^bf\left(z(t)\right)z'(t)\,dt. \end{eqnarray} Here we assume that $f\left(z(t)\right)$ is piecewise continuous on the interval $a \leq t \leq b$ and refer to the function $f (z)$ as being piecewise continuous on $C.$ Since $C$ is a contour, $z'(t)$ is also piecewise continuous on $a \leq t \leq b$; and so the existence of integral (\ref{contour-integral}) is ensured.
The right hand side of (\ref{contour-integral}) is an ordinary real integral of a complex-valued function; that is, if $w(t) = u(t) + i v(t),$ then \begin{eqnarray}\label{integral-real-cv} \int_a^b w(t)\,dt = \int_a^b u(t)\,dt + i \int_a^b v(t)\,dt \end{eqnarray}
Now let us write the integrand $$f(z)= u(x,y)+ iv(x,y)$$ in terms of its real and imaginary parts, as well as the differential $$dz=\frac{dz}{dt}dt = \left(\frac{dx}{dt}+ i \frac{dy}{dt}\right)dt = dx+ i dy$$ Then the complex integral (\ref{contour-integral}) splits up into a pair of real line integrals:
Example 1: Let's evaluate $\int_C \overline{z}\, dz,$ where $C$ is given by $x=3t, y=t^2,$ with $-1\leq t\leq 4.$
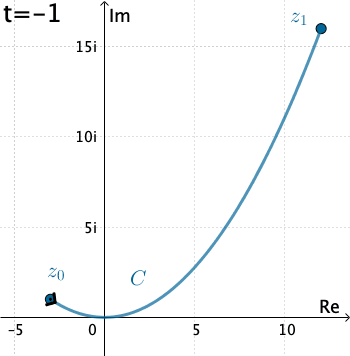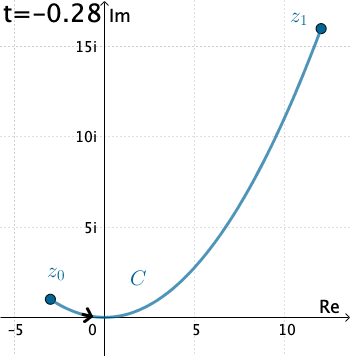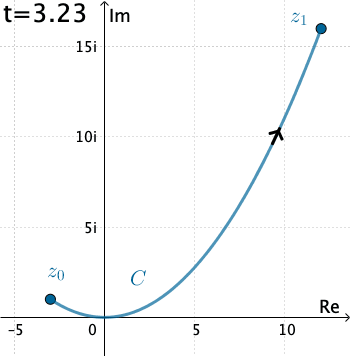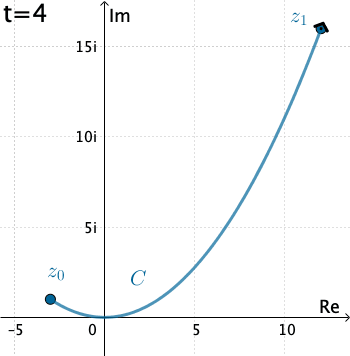
Here we have that $C$ is $z(t)=3t+ it^2 .$ Therefore, with the identification $f(z)=\overline{z}$ we have $$f\left(z(t)\right)=\overline{3t+it^2}= 3t-it^2 .$$ Also, $z'(t) = 3 + 2it,$ and so the integral is \begin{eqnarray*} \int_C \overline{z}\, dz&=& \int_{-1}^4 \left(3t-it^2\right)\left(3+ 2it\right)dt\\ &=& \int_{-1}^4 \left(2t^3+9t + 3t^2i\right)dt\\ &=& \int_{-1}^4 \left(2t^3+9t \right)dt + i\int_{-1}^4 3t^2dt\\ &=& \Bigg. \left(\frac{1}{2}t^4 + \frac{9}{2} t^2\right)\Bigg|_{-1}^4 + i\Bigg. t^3\Bigg|_{-1}^4\\ &=& 195+ 65 i. \end{eqnarray*}
Example 2: Now let's evaluate $\displaystyle \int_C \dfrac{1}{z}\, dz,$ where $C$ is the circle $x=\cos t, y=\sin t,$ with $0\leq t\leq 2\pi .$
In this case $C$ is $z(t)=\cos t + i \sin t = e^{it},$ $$f\left(z(t)\right)=\frac{1}{e^{it}}$$ and, $z'(t) = ie^{it}.$ Thus \begin{eqnarray*} \int_C \dfrac{1}{z}\, dz&=& \int_{0}^{2\pi} \left(e^{-it}\right)ie^{it}dt = i \int_{0}^{2\pi} dt= 2\pi \,i. \end{eqnarray*}
Numerical evaluation of complex integrals
Exploration 1
Use the following applet to explore numerically the integral $$\int_C \overline{z}\, dz$$ with different contours $C$:
- Line segments.
- Semicircles.
- Circles, positively and negatively oriented.
You can also change the domain coloring plotting option. Drag the points around and observe carefully what happens. Then solve Exercise 1 below.
The arrows on the contours indicate direction.
Exercise 1: Use definition (\ref{contour-integral}) to evaluate $\displaystyle \int_C \overline{z}\, dz,$ for the following contours $C$ from $z_0=-2i$ to $z_1=2i$:
- Line segment. That is, $z\left(t\right) = -2i(1-t)+ 2it,$ with $0\leq t\leq 1.$
- Right-hand semicircle. That is, $z\left(\theta\right) = 2e^{i \theta}$ with $-\frac{\pi}{2}\leq \theta \leq \frac{\pi}{2}.$
- Left-hand semicircle. That is, $z\left(\theta\right) = -2ie^{-i \theta}$ with $0 \leq \theta \leq \pi.$
Use the applet to confirm your results.
What conclusions (if any) can you draw about the function $\overline{z}$ from this?
Exploration 2
Now use the applet below to explore numerically the integrals
$$\int_C \left(z^2+z\right) dz;\qquad \int_C \frac{1}{z^2}\, dz$$
with different contours $C$ (line segments, semicircles, and circles).
Drag the points around and observe carefully what happens.
You can select the functions z^2+z or 1/z^2
from the list at the left-top corner.
Then solve Exercises 2 and 3.
Exercise 2: Consider the integral $$I_1 =\int_C \left(z^2+z\right) dz.$$ Use the applet to analyze the value of $I_1$ in the following cases:
- $C$ is any contour from $z_0=-1-i$ to $z_1 = 1+i.$
- $C$ is the circle with center $z_0$ and radius $r\gt 0,$
$|z-z_0|= r$; positively or negatively oriented.
In this cases select
Circle ↺orCircle ↻.
What conclusions (if any) can you draw about the value of $I_1$ and the function $z^2+z$ from this?
Exercise 3: Now considering integral
$$I_2 =\int_C \dfrac{1}{z^2}dz.$$ First, in the applet select the function
f(z)=1/z^2.
Then analyze the values of $I_2$ in the following cases:
- $C$ is any contour from $z_0=-i$ to $z_1 = i.$
What happens when you select
Line Segmentin the applet? What happens when you selectSemicircles? - $C$ is the circle with center $z_0$ and radius $r\gt 0,$
$|z-z_0|= r$; positively or negatively oriented.
In this case select
Circle ↺orCircle ↻. What happens if $z = 0$ is inside or outside the circle? What happens if $z=0$ lies on the contour, e.g. when $z_0=1$ and $r=1$?
What conclusions (if any) can you draw about the value of $I_2$ and the function $\dfrac{1}{z^2}$ from this?
Antiderivatives
Although the value of a contour integral of a function $f (z)$ from a fixed point $z_0$ to a fixed point $z_1$ depends, in general, on the path that is taken, there are certain functions whose integrals from $z_0$ to $z_1$ have values that are independent of path, as you have seen in Exercises 2 and 3. These examples also illustrate the fact that the values of integrals around closed paths are sometimes, but not always, zero. The next theorem is useful in determining when integration is independent of path and, moreover, when an integral around a closed path has value zero. This is known as the complex version of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
As a consequence of the previous Theorem 1, for closed curves we have \begin{eqnarray} \int_{C} f\left(z\right)dz=\int_{C}F^{\prime}(z) dz=0. \end{eqnarray} for every closed contour $C,$ that is, the endpoints are equal.
If the function $f(z)$ satisfies the hypothesis of Theorem 1, then for all contours $C$ lying in $D$ beginning at $z_1$ and ending at $z_2$ we have expression (\ref{FTC}). Hence the result demonstrates that the integral is independent of path. This fact is illustrated in Figure 3.
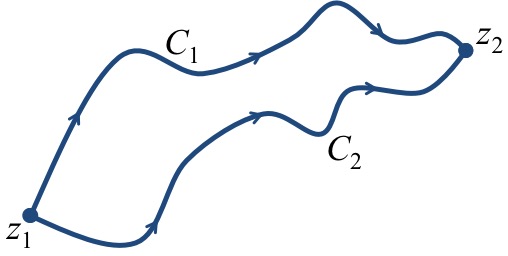
Considering Figure 3, we have $$\int_{C_1} f\left(z\right)dz=\int_{C_2} f\left(z\right)dz$$ because